How is Asthma Treated?
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the most common treatments for asthma.

Source: American Thoracic Society
Authors: Lynn Fussner, MD, Carmen Mikacenic, MD, Tamas Dolinay, MD, Benjamin Suratt, MD
Reviewers: : Jean-Marie Bruzzese, PhD, Maureen George, MSN, PhD, Marianna Sockrider, MD, DrPH.
How is Asthma treated?
Once you are diagnosed with asthma, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to control your asthma. This article describes commonly used asthma medicines and other actions you can take to control asthma.

Your Asthma Action Plan
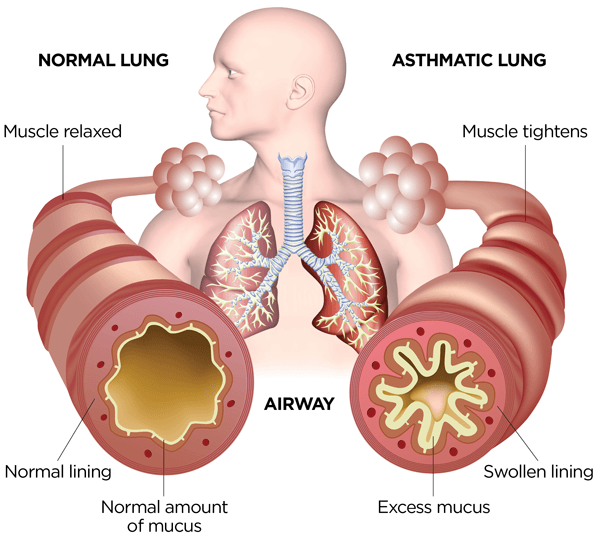
An Asthma Action Plan is a tool that you and your healthcare provider develop to help you manage your asthma. It will list your medicines, when you should take them, and how to monitor your breathing and asthma control. With asthma, there are two main problems: swelling (inflammation) of the airways, and tightening of the muscles around the airways (bronchoconstriction). Different medicines used to control asthma are designed to address both of these issues, making it easier to breathe. These medicines come in multiple forms, including inhalers, pills, and injections (shots). It is important to use your medicines exactly as instructed by your healthcare provider. You will be given a “rescue” inhaler (see below), and your healthcare provider will help you decide if you need any other types of medicine for your asthma.
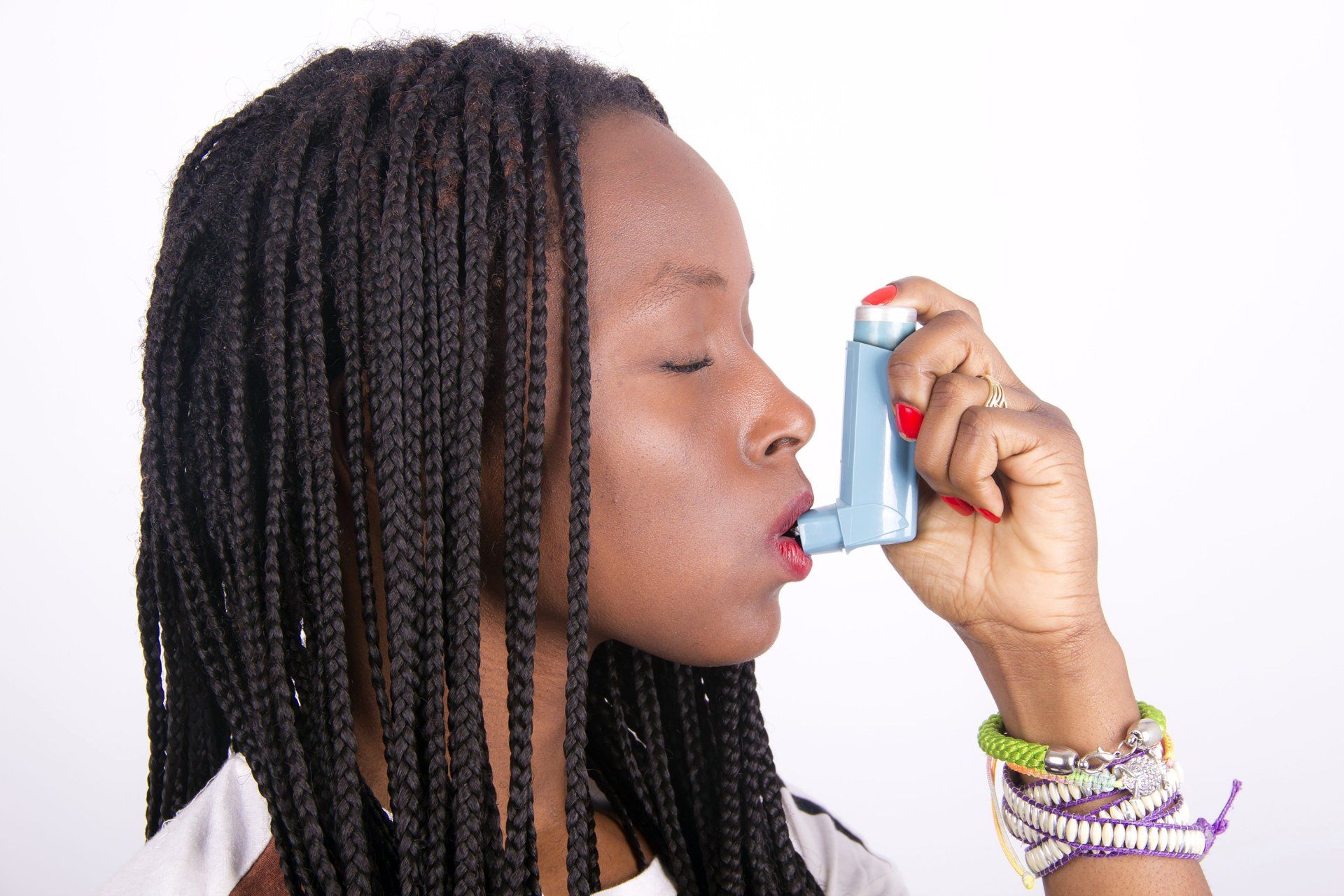
Inhaled Medicines
These most often come in the form of inhalers (sometimes called puffers), which release a dose of medicine to breathe in when you activate them. Inhaled medicine may also be given using a machine called a nebulizer, which turns liquid medication into a mist that you inhale. It is important for you to review with your healthcare provider or pharmacist the correct way to use each medicine. Remember to rinse your mouth after each use of inhalers that contain inhaled steroids.
- Short-acting inhaled medicines—also known as rescue or quick relief inhalers Short-acting medicines for asthma are bronchodilators that relax the muscles around the airways. The most common types are the shortacting beta agonists, albuterol or levalbuterol. A second type is the short-acting anti-cholinergic medicine ipratropium, which is often paired with another medicine. When used correctly, they usually start to work within 10 minutes to improve your breathing. You should keep one of these inhalers with you at all times.
- Long-acting inhaled medicines—It is important to work closely with your provider regarding the most appropriate frequency of long-acting inhaled medications for you, based on the severity and characteristics of your asthma. These are sometimes called controller medications. They work over time to keep your airway swelling (inflammation) and tightening under good control long-term.
- Inhaled steroids These treat swelling (inflammation) in the airways and keep the airways open. Examples: beclomethasone, budesonide, ciclesonide, flunisolide, fluticasone, mometasone.
- Long-acting bronchodilators These come in two categories:
- Long-acting beta agonist—Used together with inhaled steroids to keep the airways open and improve asthma control. Examples: salmeterol, formoterol, vilanterol.
- Long-acting anticholinergic—May be added for better control of asthma, to relax the muscles around the airways and decrease mucus production. Examples: tiotropium, umeclidinium.
Oral (Pill) Medications
- Leukotriene modifying medications may be used in addition to your inhaled medications, particularly if you have allergies. They do not work quickly and should not replace your inhaler(s). Examples: montelukast, zafirlukast, zileuton.
- Oral steroids, most commonly prednisone, may be used to treat a flare of your asthma, in order to reduce the swelling in your airways that makes it hard for you to breathe.
Injections
If your asthma is not well controlled using inhaled and oral medications, your asthma specialist may recommend additional medicines. These medicines affect parts of your immune system that may be contributing to your asthma symptoms. They are selected based on test results. Examples of these medicines include omalizumab, benralizumab, mepolizumab, and dupilumab.

Besides medicines, what else can be done to help control Asthma?
Taking an active role in the management of your asthma by partnering with your healthcare provider will help you to breathe easier. It is important to follow your asthma action plan and take your medicines as prescribed. There are other things you can do to help manage your asthma.
These include:
- Thinking about your environmental triggers
- Avoiding irritants like tobacco smoke or vape
- Managing your allergies
Irritants & Triggers
Identify which exposures and experiences seem to trigger your asthma so that you can avoid them when possible. It may be helpful to keep a journal of your activities and symptoms to help find patterns. It is very important to avoid exposure to or stop any smoking or vaping.
Lifestyle
Regular exercise is an important part of managing your asthma and staying healthy. It can also help to decrease stress. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to exercise safely with asthma. You may also consider learning more about ways to control any excess stress, as stress can contribute to your asthma symptoms.
Vaccines
Get a flu shot (vaccine) every year to prevent the flu or reduce the severity of the flu. You may also ask your healthcare provider if a pneumococcal vaccine to prevent a type of bacterial pneumonia is right for you.