About our Practice
Pulmonary Medicine
What is pulmonary medicine?
Pulmonary medicine is a field of medicine that deals with conditions of the respiratory system. A doctor who specializes in pulmonary medicine is known as a pulmonologist. Our practice is staffed with nine physicians who are board certified pulmonologists and have decades of combined experience treating pulmonary diseases.
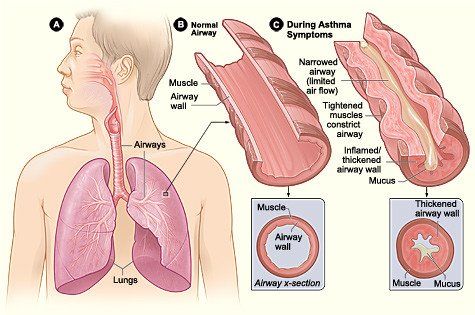
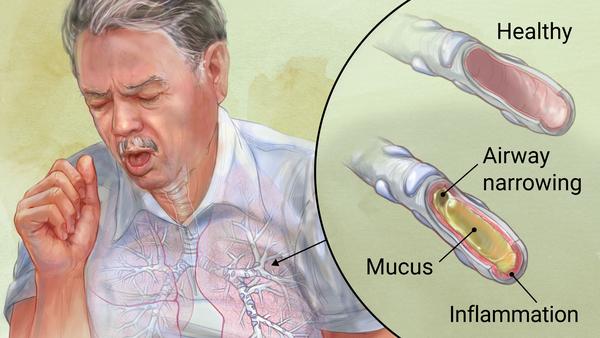
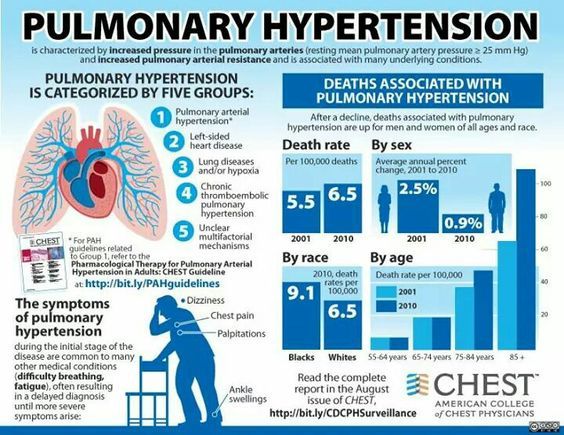
Most often, pulmonary medicine involves conditions which affect the lungs, such as lung cancer, emphysema, pneumonia, and pulmonary fibrosis. However, the respiratory system, in addition to your lungs, includes your nose, throat, trachea, airways, muscles, and blood vessels. Each of these areas are capable of becoming impacted by disease and resulting in conditions which can hinder breathing. Some examples of these sorts of conditions include, asthma, chronic rhinitis, pulmonary hypertension, and bronchitis.
Regardless of the cause for your breathing difficulties, diseases which hinder your respiratory system can be frustrating to endure and somewhat difficult to resolve. Our professional team of caring physicians will help diagnose the cause of your breathing difficulties and develop an effective treatment plan to help resolve your pulmonary issues.

What are some common examples of pulmonary diseases?
Since pulmonary medicine deals with numerous organs and supporting systems which impact breathing, there is quite an extensive list of diseases which affect breathing. However, there is a much shorter list of more common pulmonary diseases which are much more likely to impact a larger percentage of the population. The table below will outline some of the more common pulmonary diseases which impact our communities and are regularly diagnosed and treated in our clinic.